CLIP-Fields- Weakly Supervised Semantic Fields for Robotic Memory
疑问:
- 和LERF [[LERF- Language Embedded Radiance Fields]] 的区别
是什么
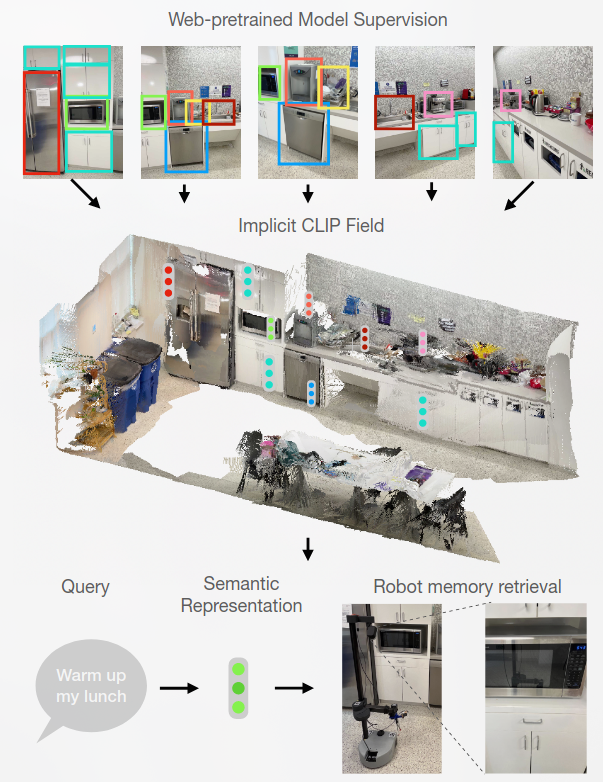
A spatial-semantic memory
是一个隐式场景模型,可用于各种任务,例如分割、实例识别、空间语义搜索和视图定位
CLIP-Fields 学习从空间位置到语义嵌入向量的映射。
这种映射可以仅通过来自网络图像和网络文本训练模型(例如 CLIP[[CLIP多模态预训练模型]]、Detic 和 Sentence-BERT)的监督进行训练;因此不使用直接的人类监督。
基于的工作
- CLIP [[CLIP多模态预训练模型]] : 基于训练一对图像和语言嵌入网络,使得图像和描述该图像的文本字符串具有相似的嵌入。 在这项工作中大量使用 CLIP 模型和嵌入,因为它们可以作为对象的视觉特征及其可能的语言标签之间的共享表示。
- Detic : 开放标签对象检测和图像分割,允许用户在运行时定义标签集,无需额外的训练或微调。用于生成数据集
- Sentence-BERT : 用于文本相似性的句子嵌入网络
- Instant-NGP : 构建了从空间(可能还有时间)坐标到某些物理属性的映射,例如神经辐射场情况下的 RGB 颜色和密度,或即时有符号距离场情况下的有符号距离
方法
Goal
We aim to build a system that can connect points of a 3D scene with their visual and semantic meaning.
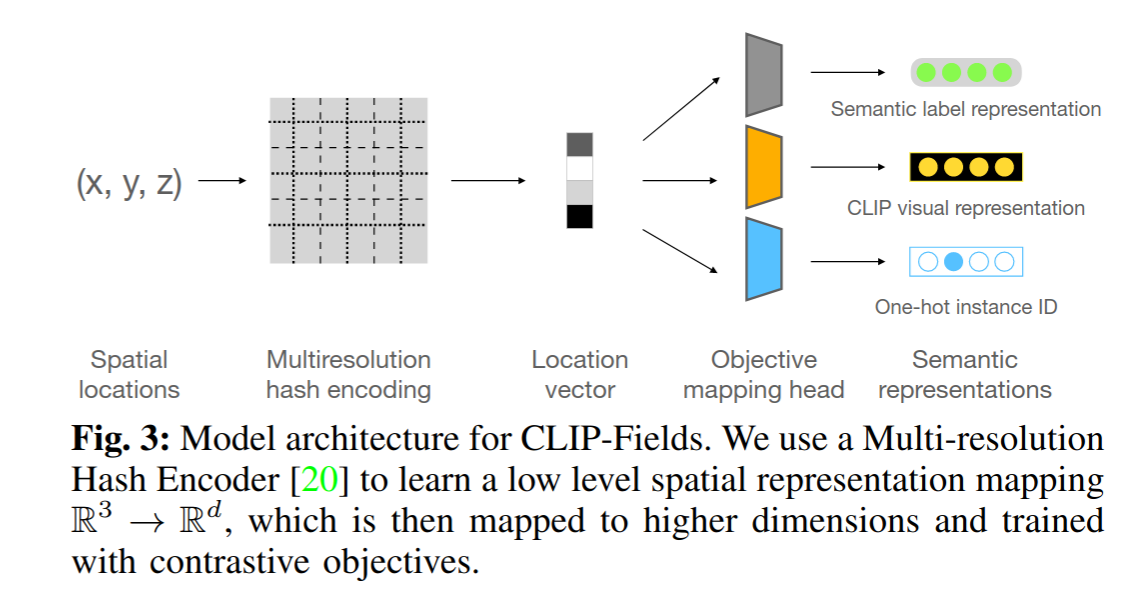
Provide an interface with a pair of scene-dependent implicit functions $f, h : R^3 → R^n$ such that for the coordinates of any point P in our scene, f (P ) is a vector representing its semantic features, and h(P ) is another vector representing its visual features.
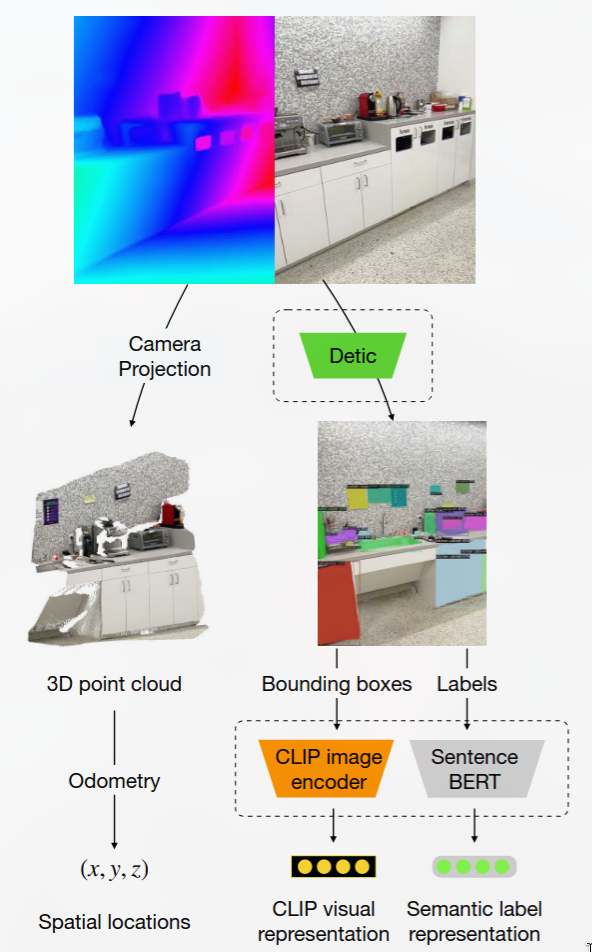
Dataset creation
> **MHE** is multi-resolution hash encoding (MHE) as introduced in [[Instant Neural Graphics Primitives with a Multiresolution Hash Encoding]]. > MHEs build an implicit representation over coordinates with a feature pyramid like structure, which can flexibly maintain both local and global information, unlike purely voxel-based encodings ([[Scene-LLM]]) which focuses on local structures only.貌似每针对一个新场景都需要重新train一遍来获得坐标到语义的映射。
CLIP-Fields- Weakly Supervised Semantic Fields for Robotic Memory